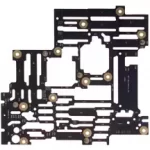
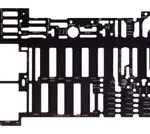
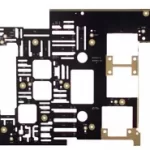
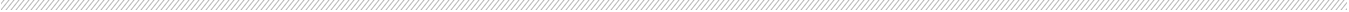Increasing surface area increases cooling capacity
Photo etching is a very effective means of producing parts with complex topographies such as heat transfer, exchange and radiating devices. Surface area is a key aspect of the rate of thermal conductivity for a particular mass. The ability to create etched features such as raised pin fins, channels and other surface effects during the etching process has a relatively minor effect on mass, but can have a dramatic impact on surface area.
In the example pictured below, about 2,000 etched pin fins increase the effective surface area by nearly 25%. This particular plate, photo-etched in aluminum and used on the space shuttles, has radiating surfaces on both sides.
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF MATERIALS
- Thermal conductivity is expressed in watts/meter*Kelvin (W/m*K).
- Pure aluminum (1100 series) is 247
- Copper is 398,
- Silver is 428
- Diamond is an astounding 2500 watts
Alloying and temper will affect thermal conductivity.
All other things being equal, a copper device will be three times heavier than an aluminum one.
CONARD’S ETCHING RANGE
- Aluminum up to .080” thick
- Copper up to .063” thick.
Locational tolerances, regardless of material thickness will be +/-.001” to drawing nominal. Dimensional tolerances at .063” will run +/-.012” and up to +/-.016″ at .080″.
APPLICATIONS FOR ETCHED THERMAL DEVICES
- Cryo cooling, commercial refrigeration, heat exchangers
- LED lighting, electronics, printed circuit boards